Microsoft Office 2019 displays commands in a series of icons stored on different tabs. This combination of icons and tabs is known as the Ribbon interface, which appears in Word, PowerPoint, Excel, Outlook, and Access. The following tables show the commands grouped under each ribbon tab for each of the five programs. Here are the. Manage both Mac and PC computers in Microsoft SCCM. This approach works best for organizations that already use Microsoft SCCM to manage PC. However, Microsoft SCCM alone has only a few features for managing Mac devices—not enough for managing Mac in enterprise. SCCM allows for the following: Setting up support and enrolling macOS clients. If you're the Microsoft 365 admin of an Office for business plan, users in your organization can only install Office using the steps in this topic as long as your plan includes the desktop version of Office, and you've assigned the user a license and given them permission to install Office (Manage software download settings in Microsoft 365).
Office Tab Enterprise Key
To read this blog post in Spanish, please click here.
Apple® Mac devices are growing in corporate popularity by the day. It’s up to IT departments to make sure that these devices utilize all resources in the environment, as well as ensure they’re visible and managed.
This can be a challenge, as Mac and Windows are very different, and Mac devices remain a minority in Windows-dominant environments. Determining how to incorporate Mac into a Windows infrastructure includes a number of factors, such as: the number of devices that need support; what type of access they require; and what tools and systems an organization already has. IT departments also need to figure out how to integrate Mac with existing Windows and Active Directory domains.
In Windows-centric organizations, managing Mac is not the highest priority on the IT project list for a variety of reasons. Few IT teams have expertise in managing Mac. Familiar techniques for managing PCs don’t help, and the best practices for dealing with Mac in a complex enterprise infrastructure can be convoluted and are not widely known.
IT teams take four main approaches when trying to accommodate Mac devices:
- Incorporate Mac devices into the Active Directory (AD) domain using existing tools meant for Windows computers.
- Use special third-party tools to manage Mac devices in the AD domain.
- Manage Mac like mobile devices.
- Manage both Mac and PC computers in Microsoft SCCM.
Some teams decide to have unmanaged macOS® devices in the environment, but this is a big security risk. You won’t necessarily lose a job if a Mac gets hacked and your infrastructure becomes vulnerable, but this can be destructive in many other ways.
Let’s take an in-depth look at these four approaches to managing Mac devices in a Windows environment.
1.Incorporate Mac devices into the Active Directory domain using existing tools.
This is the preference of many IT administrators. It’s possible to a certain degree; Mac desktops and laptops include the client component necessary to join AD and other standards-based directory services. Binding a Mac to the domain is relatively simple. Windows Server automatically creates the computer object in AD (unless it already exists), just like it would with a Windows desktop.
Recent macOS releases make it even easier to integrate Apple products, as the OS can work with Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) and Microsoft Exchange ActiveSync.
The fact remains, however, that Mac computers are not Windows desktops, and most management products are built for Windows. Native SCCM capabilities for Mac devices are limited and insufficient for full macOS lifecycle management. Compatibility issues inevitably come up. One way to smooth these issues is to extend the AD schema to better accommodate Mac computers. However, that requires development resources and technical expertise beyond what many companies can commit, especially if Mac devices are in the minority.
2. Use special third-party tools to manage Mac devices in the AD domain.

AD and command support in macOS make integrating Mac devices easier, but many administrators still like to use other tools to help with management. For example, IT admins can join Mac devices to AD domains and then use Apple Remote Desktop™ to push commands out to Mac clients.
Office Tab Enterprise Torrent
An alternative is to implement Mac OS X® Server on its own system; Apple Profile Manager can then be used to set Mac policies based on AD groups. This entails setting up an Apple Open Directory domain alongside the AD service, which can make management easier in the long term. The Mac devices are still bound to AD, so there is seamless communication between the two environments, as well as shared file and printer services.
If this sounds too complicated, there is Centrify User Suite (Mac Edition), which can administer Mac devices and centrally manage authentication, policy enforcement, and single sign-on. Another option is Jamf Pro, a comprehensive endpoint management product.
3. Manage Mac like mobile devices.
Apple is moving toward a mobile device management (MDM) model, rather than a traditional directory services model. This means that IT admins can use the same management tools on Mac computers, iOS, and Android devices.
The new Apple MDM framework allows administrators to initiate AirPlay® sessions on managed devices and push enterprise applications to Mac computers. Improved OS X Server and platform capabilities also make it more MDM-friendly. Users can register Mac devices, and vendors can make use of a greater number of application programming interfaces available to third-party security and management solutions.
Many MDM vendors have quickly embraced new Mac features, such as VMware AirWatch. AirWatch allows admins to manage Mac computers alongside smartphones and tablets and perform a wide variety of tasks.
Organizations can also implement a separate tool, such as MobileIron or an Apple server not bound to AD. This allows IT admins to implement user access through virtual private networks without having to join the devices to the domain. This is useful when incorporating users’ personal Mac laptops.
4. Manage both Mac and PC computers in Microsoft SCCM.
This approach works best for organizations that already use Microsoft SCCM to manage PC. However, Microsoft SCCM alone has only a few features for managing Mac devices—not enough for managing Mac in enterprise. SCCM allows for the following:
- Setting up support and enrolling macOS clients.
- Deploying settings to macOS clients.
- Performing hardware inventory of macOS clients.
- Deploying applications to macOS clients.
While SCCM is capable of managing these devices, additional items need to be installed and configured to support Mac. You’ll need to implement a public key infrastructure for Active Directory Certificate Services. These certificates are used to communicate with SCCM through SSL communications. Each Mac with a SCCM client installed acts like an Internet-based client.
Since the Mac devices are acting like Internet-based clients, you’ll need to have a Configuration Manager Site server with a fully qualified domain name, as well as a minimum of one HTTPS-enabled management point and one HTTPS-enabled distribution point.
You’ll also need to configure the enrollment point and enrollment proxy point features in SCCM. This will allow your macOS clients to be enrolled in the SCCM environment after the client is installed. In order to enable the management of these macOS clients, you’ll need to configure custom client settings.
SCCM’s built-in support for Mac OS does work great, but there are certain limitations to the features and functionality of this support. To manage Max OS X clients, you must have PKI infrastructure and additional SCCM site systems. If you’re not planning on enabling HTTPS communications for your entire corporate environment, you’ll need to have multiple management points and distribution points. One management point will be configured for HTTP communications, and one will be configured for HTTPS communications, as is the same for the multiple distribution points.
Extend SCCM for Enterprise-Level Mac Management
What if you could add the same right-click management that Windows devices receive in SCCM to Mac devices? What if you could do it with a short learning curve, no silos, and the same system administrators?
There is a solution that can do all of this and more: Parallels® Mac Management for Microsoft® SCCM. Parallels Mac Management gives SCCM all the missing tools for Mac management, including FileVault® 2 encryption, macOS deployment, application delivery, Apple Device Enrollment Program, and compliance via SCCM configuration items and baselines.
With Parallels Mac Management, you simply add full macOS lifecycle management to Microsoft SCCM and manage PC and Mac computers in a single pane of glass. There’s a minimum learning curve and no additional infrastructure required. The solution leverages your Microsoft SCCM investments and enables Windows admins to manage Mac computers.
For further information on Parallels Mac Management, please feel free to contact our sales team to request a free trial.

Include Components: | Office Tab Enterprise | Office Tab |
| Tabs for Word | ||
| Tabs for Excel | ||
| Tabs for PowerPoint | ||
| Tabs for Publisher | ||
| Tabs for Access | ||
| Tabs for Project | ||
| Tabs for Visio |
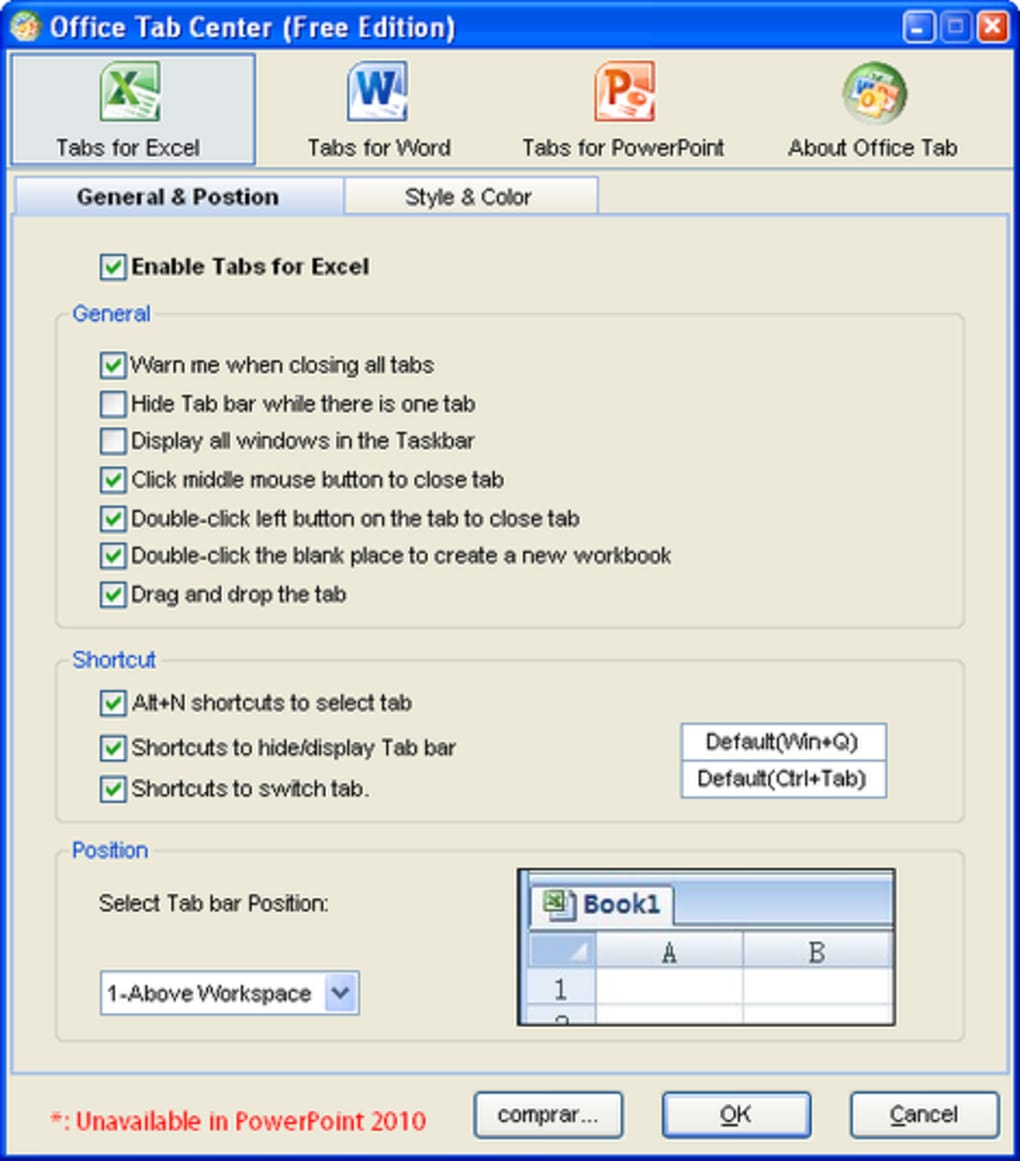
Save All in One ClickA key advantage of Office Tab is that you can save time by consolidating your actions! For example, if you've opened multiple files, you don’t have to save and close them individually; just click 'Save All' from the Context menu and all your files are saved. Want to close all opened files? Simply select 'Close All” and all your files will be closed. |
In Office Tab, you can add a saved Microsoft Office file to a group. You can quickly open a group of documents or a group of Excel files and so on. With this Favorites Group feature, you can apply the following operations to a group of documents in Microsoft Office applications easily. Add a document to a group; |
Rename Files EasilyYou don’t have to open the 'Save As' dialog to rename a file. Just click 'Rename' on the Context Menu in the tab and enter the new file name—it’s that simple! If you want to save the file in another folder, select 'Save As' from the Context Menu. |
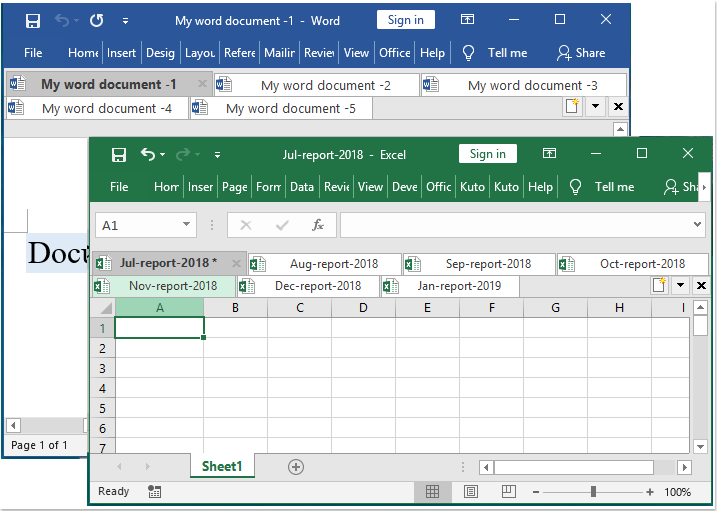
Displays Full File NameIf a file name is long, typically, the Windows taskbar displays only a small part of it, which is often a problem. However, with Office Tab installed, you will able to see the entire file name on the Tab Bar, no matter how long it is. |
Useful Context MenuRight-click on a tab or Tab Bar to access the tab/tab bar context menu. Office Tab also combines some common command items in Microsoft Office, letting you access those items more quickly. |
Easy-to-useThe tabbed interface allows you to open multiple documents in a single window. Each document appears as a new tab within the window (not a new window) and can be accessed with one click. This feature improves your efficiency when working with Microsoft Office programs (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Project, Publisher, Access and Visio). |
High PerformanceOffice Tab is based on the standard Microsoft Office Add-in Technology. It does not impact the performance of the standard application and has an extremely small file size. |
Move TabsTabs can be moved easily by dragging. You can switch between tabs using the mouse or you can activate a tab by pressing Alt + N (“N” being the tab order '1, 2, 3…'). |
Customize Tab AppearanceThe colors of the tabs and the Tab Bar are customizable. There are 11 styles for you to choose from. Within each style, the font style and the name of each tab can be changed to suit your preference (to apply these changes, you will need to close and restart Microsoft Office). |

